Correct Gamma Settings for Texture Maps in Corona Renderer
Introduction
If you’ve ever applied a texture in Corona Renderer and noticed that it looks too dark, too washed out, or just plain wrong, you’re not alone! The culprit is often incorrect gamma settings. Getting the right gamma settings in Corona Renderer is key to achieving realistic material rendering. This guide will walk you through the correct gamma settings for texture maps, how to fix gamma issues in Corona Renderer, and ensure your materials look accurate.
📌 Related Article: IOR in Corona Renderer: A Complete Guide for Realistic Materials – Discover how IOR values affect reflections and material realism in Corona Renderer.
Why is Gamma Correction Important in Rendering?
Gamma correction plays a crucial role in realistic material rendering because it ensures that textures appear as they would in the real world. Without proper gamma settings in Corona Renderer, you might experience:
- Inaccurate lighting effects (too bright or too dark materials)
- Loss of detail in textures
- Unnatural reflections and refractions
- Distorted displacement and bump effects
By applying the correct texture map gamma correction in Corona Renderer, you can make sure that textures interact properly with lighting and materials, producing physically correct results.
Understanding Gamma in Corona Renderer
Think of gamma correction as a way to tell Corona how to interpret your textures. Some textures contain color information, while others hold technical data (like bump or roughness). These two types of textures need to be handled differently to ensure they behave correctly in your scene.
Corona uses two primary gamma settings:
- Gamma 2.2 (sRGB) → Used for textures that affect color (Diffuse, Albedo, Emission). This ensures they look natural in lighting conditions.
- Gamma 1.0 (Linear) → Used for textures that affect surface behavior (Bump, Normal, Glossiness, Roughness, etc.). These contain non-color data and should not be gamma corrected.
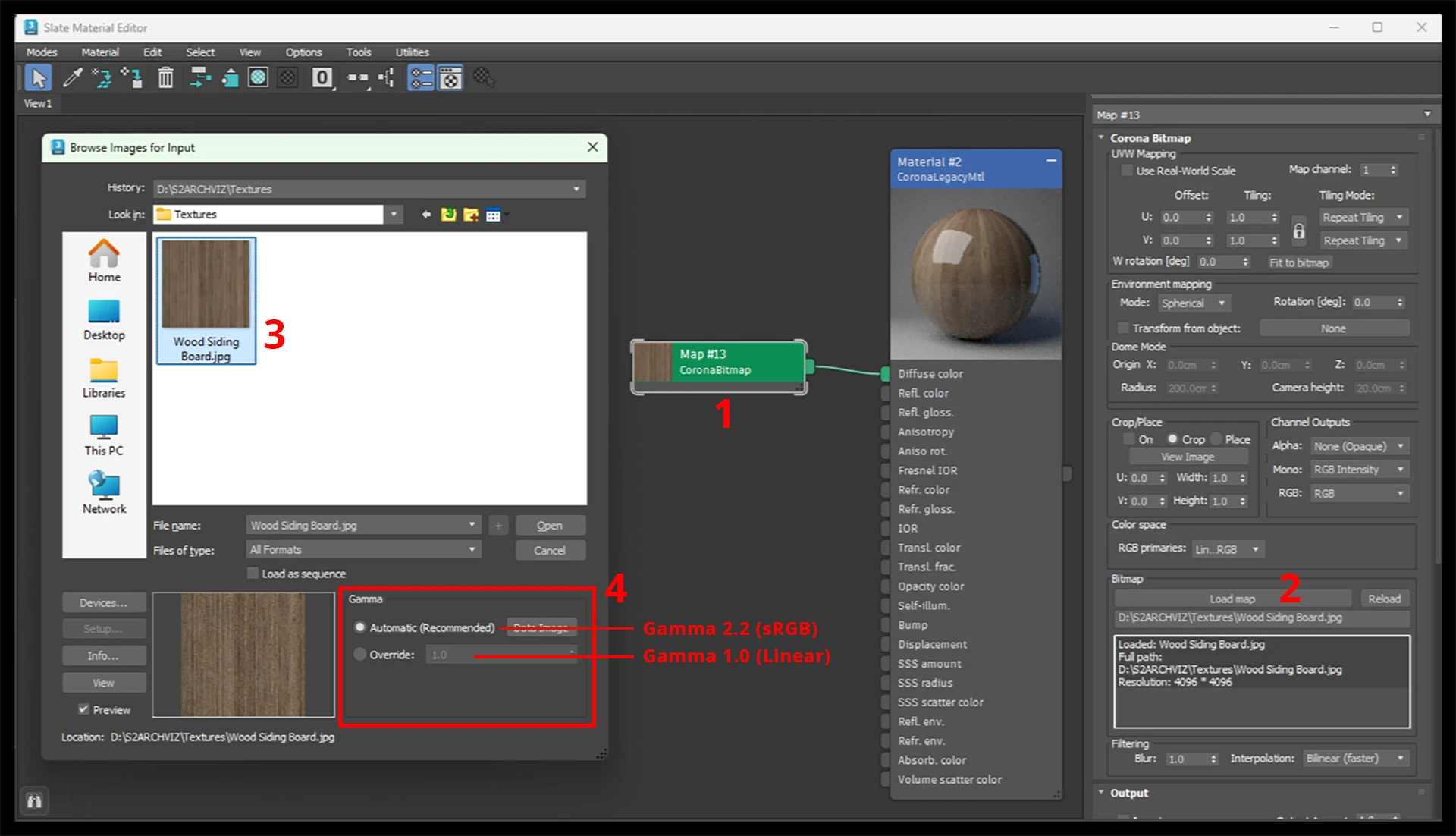
Correct Gamma Settings for Different Texture Maps
Below is the comprehensive table outlining the best gamma settings for PBR materials and texture maps in Corona Renderer:

Common Mistakes and How to Fix Them
❌ Applying Gamma 2.2 to Non-Color Maps
- What Happens? Weird reflections, strange bump behavior, or incorrect displacement.
- Fix: Always use Gamma 1.0 for technical maps like bump, glossiness, and reflection.
❌ Forgetting to Override Gamma in the Bitmap Loader
- What Happens? Some textures may load with the wrong gamma, making them look unnatural.
- Fix: Manually check and override gamma settings when necessary.
❌ Using Color Maps in Linear Workflow
- What Happens? Diffuse textures may look too dark or washed out.
- Fix: Always use sRGB (Gamma 2.2) for color textures.
Best Practices for Gamma Correction in Corona Renderer
- ✅ Always verify gamma settings in the Material Editor before rendering.
- ✅ Use high-quality textures from reliable sources to avoid incorrect gamma encoding.
- ✅ Test your materials in different lighting conditions to catch gamma-related issues early.
- ✅ Understand how gamma correction integrates with PBR workflows in other render engines like V-Ray, Unreal Engine, and Blender.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
🔹 Why do my textures look too dark in Corona Renderer?
- This usually happens if sRGB textures (Diffuse, Albedo, etc.) are loaded with Gamma 1.0. Make sure they are set to Gamma 2.2.
🔹 How do I fix washed-out textures in my renders?
- Check if your textures are incorrectly gamma-corrected. If they look too bright or desaturated, they may have been saved with double gamma correction (avoid applying Gamma 2.2 twice).
Conclusion
Mastering gamma settings in Corona Renderer is a simple but powerful way to get the most out of your materials. By applying the correct gamma settings for texture maps, you can achieve more accurate reflections, realistic surface details, and physically correct lighting interactions. The key takeaway? Color maps need Gamma 2.2, while grayscale maps need Gamma 1.0. Get this right, and your renders will thank you!
📌 Related Article: IOR in Corona Renderer: A Complete Guide for Realistic Materials – Discover how IOR values affect reflections and material realism in Corona Renderer.
For more tips, check out our Visualization Techniques and Tutorials section of S2ArchViz Stories. Happy rendering! 🚀


